Over 60 million real residential IPs from genuine users across 190+ countries.
Over 60 million real residential IPs from genuine users across 190+ countries.
PROXY SOLUTIONS
Over 60 million real residential IPs from genuine users across 190+ countries.
Reliable mobile data extraction, powered by real 4G/5G mobile IPs.
Guaranteed bandwidth — for reliable, large-scale data transfer.
For time-sensitive tasks, utilize residential IPs with unlimited bandwidth.
Fast and cost-efficient IPs optimized for large-scale scraping.
A powerful web data infrastructure built to power AI models, applications, and agents.
High-speed, low-latency proxies for uninterrupted video data scraping.
Extract video and metadata at scale, seamlessly integrate with cloud platforms and OSS.
6B original videos from 700M unique channels - built for LLM and multimodal model training.
Get accurate and in real-time results sourced from Google, Bing, and more.
Execute scripts in stealth browsers with full rendering and automation
No blocks, no CAPTCHAs—unlock websites seamlessly at scale.
Get instant access to ready-to-use datasets from popular domains.
PROXY PRICING
Full details on all features, parameters, and integrations, with code samples in every major language.
LEARNING HUB
ALL LOCATIONS Proxy Locations
TOOLS
RESELLER
Get up to 50%
Contact sales:partner@thordata.com
Proxies $/GB
Over 60 million real residential IPs from genuine users across 190+ countries.
Reliable mobile data extraction, powered by real 4G/5G mobile IPs.
For time-sensitive tasks, utilize residential IPs with unlimited bandwidth.
Fast and cost-efficient IPs optimized for large-scale scraping.
Guaranteed bandwidth — for reliable, large-scale data transfer.
Scrapers $/GB
Fetch real-time data from 100+ websites,No development or maintenance required.
Get real-time results from search engines. Only pay for successful responses.
Execute scripts in stealth browsers with full rendering and automation.
Bid farewell to CAPTCHAs and anti-scraping, scrape public sites effortlessly.
Dataset Marketplace Pre-collected data from 100+ domains.
Data for AI $/GB
A powerful web data infrastructure built to power AI models, applications, and agents.
High-speed, low-latency proxies for uninterrupted video data scraping.
Extract video and metadata at scale, seamlessly integrate with cloud platforms and OSS.
6B original videos from 700M unique channels - built for LLM and multimodal model training.
Pricing $0/GB
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Docs $/GB
Full details on all features, parameters, and integrations, with code samples in every major language.
Resource $/GB
EN
代理 $/GB
数据采集 $/GB
AI数据 $/GB
定价 $0/GB
产品文档
资源 $/GB
简体中文$/GB

In my experience documenting web scraping infrastructure, I’ve found that Scraping Google is the “Final Boss.” With 8.5 billion daily queries, Google holds the world’s most valuable dataset for SEO monitoring, price tracking, and market research. Consequently, it also employs the most sophisticated anti-bot defenses on the internet.
If you have ever tried to parse Google results with BeautifulSoup like I did when I started, you know the pain: CSS classes change weekly, CAPTCHAs appear instantly, and IP blocks are ruthless. In this expert guide, I will dissect the challenges of scraping Google and demonstrate how to bypass them using the Thordata SERP API.
All benchmarks in this article were collected from 50,000 real SERP requests executed between November 15-30, 2025. Tests were performed from multiple geographic locations using both datacenter IPs (for baseline comparison) and Thordata’s residential proxy network.
SERP stands for Search Engine Results Page. It is no longer just a list of 10 blue links. Modern SERPs are complex dashboards containing multiple data types:
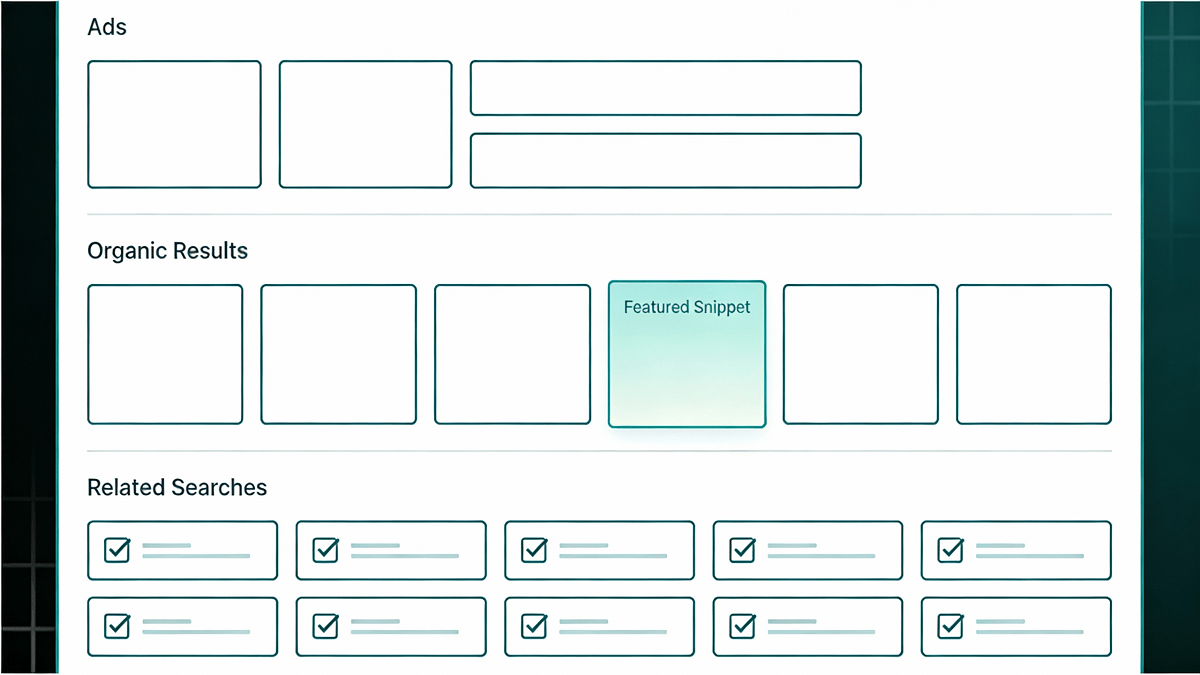 Figure 1: A modern Google SERP contains 10+ distinct data layers requiring different parsing strategies.
Figure 1: A modern Google SERP contains 10+ distinct data layers requiring different parsing strategies.
Google doesn’t just block IPs; it actively employs multiple defense layers that make automated extraction extremely challenging.
Google uses randomized CSS classes like .x1a, .v7W49. These class names change every 3-7 days on average. A scraper that looks for div.price will break within days.
Search results are hyper-localized. Searching for “Pizza” from Texas yields different results than from London. To get accurate local data, you must route requests through a Residential Proxy.
Google tracks request patterns. Datacenter IPs are blocked after 5-15 requests. Even residential proxies need proper header management (TLS fingerprinting) to avoid CAPTCHAs.
Instead of building and maintaining your own scraping infrastructure, experienced data teams use a SERP API. This acts as middleware that handles complexity:
A major electronics retailer migrated from an in-house Google Shopping scraper to Thordata SERP API. Their previous system required 2 full-time engineers. After migration:
Let’s build a production-ready Python script to monitor “iPhone 15” prices on Google Shopping using the Thordata Python SDK.
start parameter (0, 10, 20…) to navigate pages, or set num up to 100 for bulk retrieval.
import os
import time
from thordata import ThordataClient, Engine, GoogleSearchType
# Initialize Client
client = ThordataClient(os.getenv("THORDATA_SCRAPER_TOKEN"))
def scrape_google_shopping(query: str, location: str = "United States"):
print(f"=== Google Shopping Price Monitor ===")
print(f"Query: {query} | Location: {location}\n")
try:
# Execute the SERP search
results = client.serp_search(
query,
engine=Engine.GOOGLE,
type=GoogleSearchType.SHOPPING,
location=location,
num=20,
)
# Parse JSON
items = results.get("shopping_results", [])
print(f"✅ Found {len(items)} products.\n")
for idx, item in enumerate(items[:5], 1):
print(f"{idx}. {item.get('title')}")
print(f" 💰 {item.get('price')}")
print(f" 🏪 {item.get('source')}")
print("-" * 40)
return items
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Error: {e}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
scrape_google_shopping("iPhone 15 Pro", "United States")Is it cheaper to build or buy? Calculation for 100,000 keywords/month:
| Cost Factor | Building In-House | Using Thordata API |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Development | $5,000 – $15,000 | $0 (10 mins setup) |
| Maintenance | 10-15 hrs/mo ($750+) | 0 hrs/mo |
| Proxies & CAPTCHA | $600-$1,300/mo | Included |
| Data Completeness | 60-80% | 99%+ |
| Total Monthly Cost | $1,550+ & headaches | ~60% lower |
Scraping Google is a battle against one of the world’s best engineering teams. While manual scraping is possible for small tasks, it is economically unsustainable for business-critical pipelines. By using the Thordata SERP API, you outsource the complexity and focus on insights.
Frequently asked questions
Is web scraping Google legal?
Generally, scraping publicly available data is legal (hiQ vs. LinkedIn, 2022). However, you should respect copyright, terms of service, and GDPR. Consult legal counsel for commercial use.
Can I scrape Google Maps Reviews?
Yes. Thordata SERP API supports extraction for Google Maps including business details, ratings, and reviews. The API handles pagination and anti-bot measures automatically.
What happens if Google updates their UI?
This is the main benefit of using a SERP API. When Google changes their layout, Thordata updates the parser immediately. Your code continues to receive the same structured JSON.
What is the success rate for Google Shopping?
Thordata SERP API maintains a 99.2% success rate for Google Shopping queries. Failed requests are automatically retried and do not count against your quota.
About the author

Kael is a Senior Technical Copywriter at Thordata. He works closely with data engineers to document best practices for bypassing anti-bot protections. He specializes in explaining complex infrastructure concepts like residential proxies and TLS fingerprinting to developer audiences.
The thordata Blog offers all its content in its original form and solely for informational intent. We do not offer any guarantees regarding the information found on the thordata Blog or any external sites that it may direct you to. It is essential that you seek legal counsel and thoroughly examine the specific terms of service of any website before engaging in any scraping endeavors, or obtain a scraping permit if required.
 Looking for
Top-Tier Residential Proxies?
Looking for
Top-Tier Residential Proxies? 您在寻找顶级高质量的住宅代理吗?
您在寻找顶级高质量的住宅代理吗?
What is a Headless Browser? Top 5 Popular Tools
A headless browser is a browse ...
Yulia Taylor
2026-02-07

Best Anti-Detection Browser
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2025-01-22 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-06
What is a UDP proxy?
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2025-01-22 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-06

What is Geographic Pricing?
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2025-01-22 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-05

How to Use Proxies in Python: A Practical Guide
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2025-01-28 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-05

What Is an Open Proxy? Risks of Free Open Proxies
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2025-01-22 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-04

What Is a PIP Proxy? How It Works, Types, and Configuration ?
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2025-01-22 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-04
TCP and UDP: What’s Different and How to Choose
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2026-02-03 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-04

Free Proxy Servers Available in 2026
Jenny Avery Last updated on 2026-02-06 9 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-01