Over 60 million real residential IPs from genuine users across 190+ countries.
Over 60 million real residential IPs from genuine users across 190+ countries.
PROXY SOLUTIONS
Over 60 million real residential IPs from genuine users across 190+ countries.
Reliable mobile data extraction, powered by real 4G/5G mobile IPs.
Guaranteed bandwidth — for reliable, large-scale data transfer.
For time-sensitive tasks, utilize residential IPs with unlimited bandwidth.
Fast and cost-efficient IPs optimized for large-scale scraping.
A powerful web data infrastructure built to power AI models, applications, and agents.
High-speed, low-latency proxies for uninterrupted video data scraping.
Extract video and metadata at scale, seamlessly integrate with cloud platforms and OSS.
6B original videos from 700M unique channels - built for LLM and multimodal model training.
Get accurate and in real-time results sourced from Google, Bing, and more.
Execute scripts in stealth browsers with full rendering and automation
No blocks, no CAPTCHAs—unlock websites seamlessly at scale.
Get instant access to ready-to-use datasets from popular domains.
PROXY PRICING
Full details on all features, parameters, and integrations, with code samples in every major language.
LEARNING HUB
ALL LOCATIONS Proxy Locations
TOOLS
RESELLER
Get up to 50%
Contact sales:partner@thordata.com
Proxies $/GB
Over 60 million real residential IPs from genuine users across 190+ countries.
Reliable mobile data extraction, powered by real 4G/5G mobile IPs.
For time-sensitive tasks, utilize residential IPs with unlimited bandwidth.
Fast and cost-efficient IPs optimized for large-scale scraping.
Guaranteed bandwidth — for reliable, large-scale data transfer.
Scrapers $/GB
Fetch real-time data from 100+ websites,No development or maintenance required.
Get real-time results from search engines. Only pay for successful responses.
Execute scripts in stealth browsers with full rendering and automation.
Bid farewell to CAPTCHAs and anti-scraping, scrape public sites effortlessly.
Dataset Marketplace Pre-collected data from 100+ domains.
Data for AI $/GB
A powerful web data infrastructure built to power AI models, applications, and agents.
High-speed, low-latency proxies for uninterrupted video data scraping.
Extract video and metadata at scale, seamlessly integrate with cloud platforms and OSS.
6B original videos from 700M unique channels - built for LLM and multimodal model training.
Pricing $0/GB
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Docs $/GB
Full details on all features, parameters, and integrations, with code samples in every major language.
Resource $/GB
EN
代理 $/GB
数据采集 $/GB
AI数据 $/GB
定价 $0/GB
产品文档
资源 $/GB
简体中文$/GB


This guide will comprehensively teach you how to configure a proxy server on various operating systems and browsers, as well as the key factors to consider when choosing the right proxy provider, helping you smoothly embark on your first proxy server experience.
In this article, you will see:
● Definition, working principles, risks, and benefits of proxy servers
● How to configure a proxy server on popular operating systems and browsers
● How to choose the right proxy service provider
● Starting your first proxy experience
A proxy server is an intermediary system located between a user’s device and the target website (also known as a middleman). It acts as a relay for network traffic, providing users with features such as anonymous access and content filtering. Essentially, when you make a connection request to a target website through a proxy, your request is first received by the proxy server, which then forwards it to the target website. The proxy server subsequently returns the data received from the target website back to you, hiding your real IP address and adding a layer of security.
Core Functions of a Proxy
● Request Header Control: By rewriting request headers (e.g., removing or adding fields like X-Forwarded-For, Via), proxies can control the source information that the target server sees.
● Caching: By caching common resources (following mechanisms like Cache-Control, ETag), proxies can significantly reduce the latency and bandwidth consumption of repeated requests.
● Access Control: Through Access Control Lists (ACL) and authentication mechanisms, proxies can restrict who can access which resources, thereby serving as a security gateway.
Types of Proxies
By Role:
● Forward Proxy: Primarily client-side, helping clients access external resources.
● Reverse Proxy: Primarily server-side, protecting and load balancing backend services.
By Anonymity Level:
● Transparent: Does not hide the user’s IP address.
● Anonymous: Hides the user’s IP address but identifies itself as a proxy.
● High Anonymity (Elite): Hides the user’s IP address and does not identify itself as a proxy.
By Deployment Source:
● Datacenter: Hosted in datacenters.
● Residential: Uses residential IP addresses.
● Mobile: Utilizes mobile IP addresses.

The functioning of a proxy server is based on a request interception and forwarding mechanism. It receives network requests from clients, communicates with the target server on behalf of the client, and returns the response.
When you attempt to access a website, the proxy server first checks if it has a cached copy of the requested content. If it does, it directly provides the data, speeding up access and reducing bandwidth usage. If there is no cached version, the proxy forwards the request to the target server, retrieves the response, and then returns it to you. It may also cache the new data for future use.
This process ensures the following:
1. Hiding Local IP Address: Your real IP address remains concealed from the target server.
2. Data Integrity: The data transmitted is maintained and managed securely.
3. Traffic Monitoring and Control: Network administrators can monitor and control traffic effectively.
People choose proxy servers for various reasons, driven by different needs and objectives:
Cross-Border E-Commerce Price Monitoring: Sellers use proxy servers to access e-commerce sites like Amazon and eBay from different regions, enabling real-time monitoring of competitors’ prices and inventory levels to devise more accurate pricing strategies.
Content Unlocking and Bypassing Regional Restrictions: Users utilize proxies to switch to foreign IP addresses, allowing them to watch exclusive shows on platforms like Netflix and Hulu or access websites that are blocked in their region.
Large-Scale Web Crawling and Data Scraping: Researchers or businesses employ proxy servers to distribute requests, avoiding IP bans from search engines or e-commerce sites, thus efficiently collecting large amounts of structured data.
Managing Multiple Social Media Accounts: Operators use proxies to manage multiple Twitter, Instagram, or TikTok accounts under different IP addresses, reducing the risk of being banned due to unusual login activities.
Ad Placement and Verification: Advertising companies use proxies to check ad display conditions from different cities or countries, ensuring precise ad placements and identifying potential click fraud.
Now that you understand the reasons people use proxy servers, it’s also important to be aware of the potential risks associated with them.
Using a proxy server is not without its risks, as it can lead to security vulnerabilities and privacy issues.
● Free Proxy Server Traps
There’s a saying: “You get what you pay for.” Proxy servers often transmit sensitive data, and using free proxy servers can put that data at risk of being stolen by malicious actors. Some malicious proxies might even alter requests, injecting ads or harmful code. Additionally, some so-called “free” proxy servers are scams designed to steal your credit card information and passwords.
● DNS Leaks
Although user traffic passes through the proxy, DNS resolution might still be sent from the local network, exposing your actual browsing behavior. In enterprise settings, improper proxy configuration could allow unauthorized personnel to bypass security policies, increasing the risk of intrusions.
● Stability and Compliance Risks
Many proxies are unstable, leading to frequent disconnections or response delays, which can affect business continuity. Some websites have robust proxy detection mechanisms; if they detect proxy access, they may immediately ban the IP or trigger CAPTCHAs, reducing work efficiency. Moreover, if the proxy provider’s data sources are illegal, users could inadvertently cross legal boundaries, resulting in serious compliance issues.
Therefore, it is crucial to choose reputable providers and be aware of the potential risks involved.
Despite the risks associated with proxy servers, making informed choices and proper configurations can yield significant advantages that enhance efficiency for individuals and businesses.
● Improved Anonymity and Privacy Protection
By replacing or masking the client’s real IP address and cleaning up and rewriting request headers, proxies can significantly reduce the likelihood of external services tracing traffic back to individuals or devices, creating a foundational privacy barrier.
● Reduced Bandwidth Consumption and Faster Response
With effective caching strategies and connection reuse (such as keep-alive and HTTP/2), proxies can directly return cached content or reuse upstream connections for repeated requests, thereby lowering overall bandwidth usage and improving loading times.
● Centralized Policies and Access Control
Implementing authentication, rate limiting, whitelists and blacklists, and content filtering at the proxy level allows for standardized management of security and compliance policies without the need to configure each endpoint device individually.
● Enhanced Availability and Fault Tolerance
Through multi-node deployment, health checks, and load balancing mechanisms, proxies can automatically switch paths in the event of a single point of failure, maintaining service continuity and alleviating sudden traffic spikes.
● Reduced Risk of Traffic Being Identified as Anomalous
By employing dynamic allocation and rotation of IP addresses, the source of requests exhibits greater diversity, which decreases the chances of being flagged as abnormal or anomalous traffic patterns, thus enhancing the stability of long-term connections.
● Flexibility in Protocols and Forwarding
Proxies support various forwarding methods, including HTTP/HTTPS, and TCP tunneling, allowing for traffic handling at different protocol levels without requiring substantial modifications to the applications themselves.
Setting up a proxy server varies by operating system and browser. Here’s a guide for the most common platforms: Morelogin, Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, and popular browsers.
1. Morelogin
● Prevent cross-contamination of information such as cookies, caches, and IP addresses. Reduce platform risk control trigger rates and decrease account ban risks.
● Easily integrate with various proxy types, including HTTP, HTTPS.
● Automatically generate authentic and reliable browser fingerprints, which, when used with proxies, effectively prevent platform identification.
● More efficient batch management, suitable for various scenarios such as social media, e-commerce, and advertising.
● Convenient team collaboration, supporting sub-account permission management.
Download the MoreLogin and log in to your account.
Click “+ New Profile” in the left sidebar.
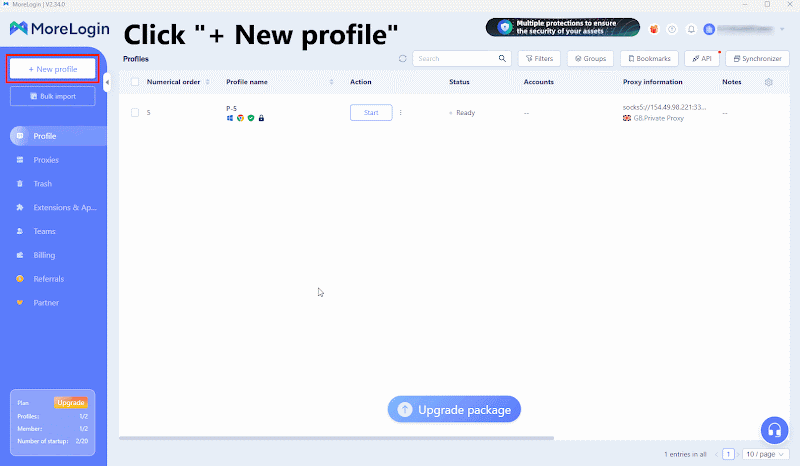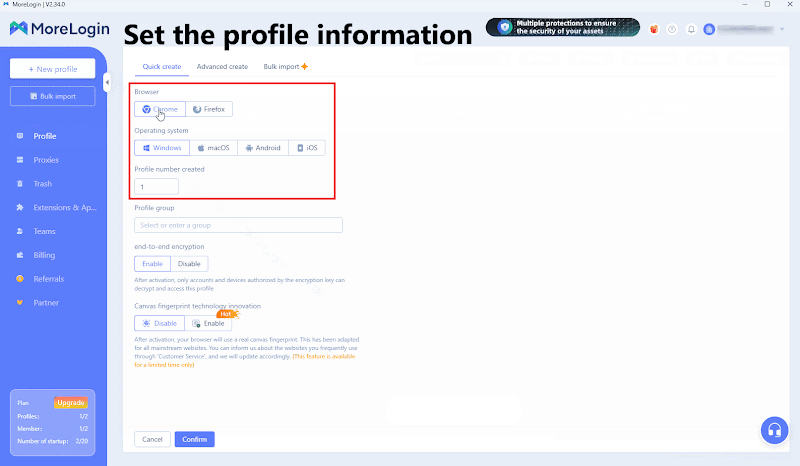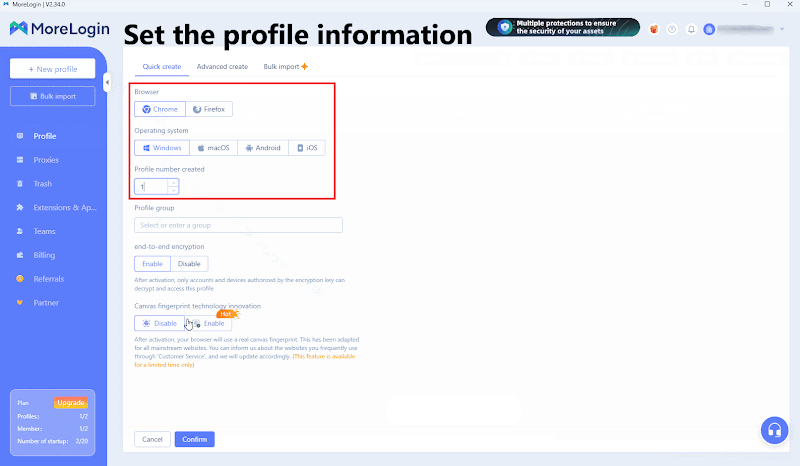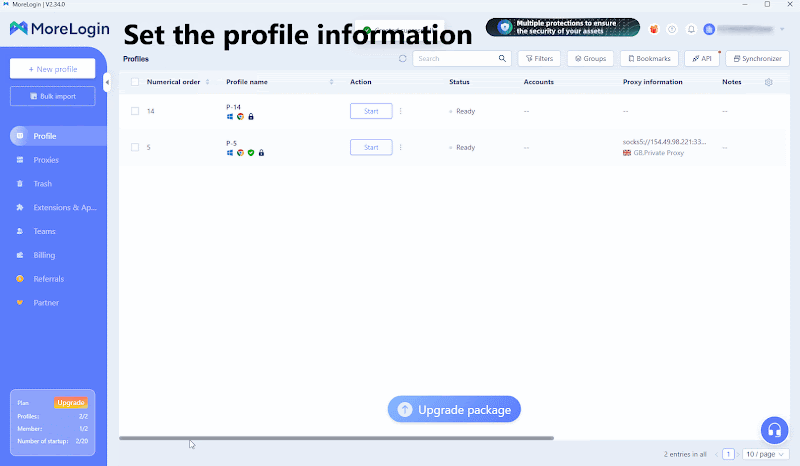
In the created profile, find “Proxy Information” and fill in the proxy information obtained from Thordata.
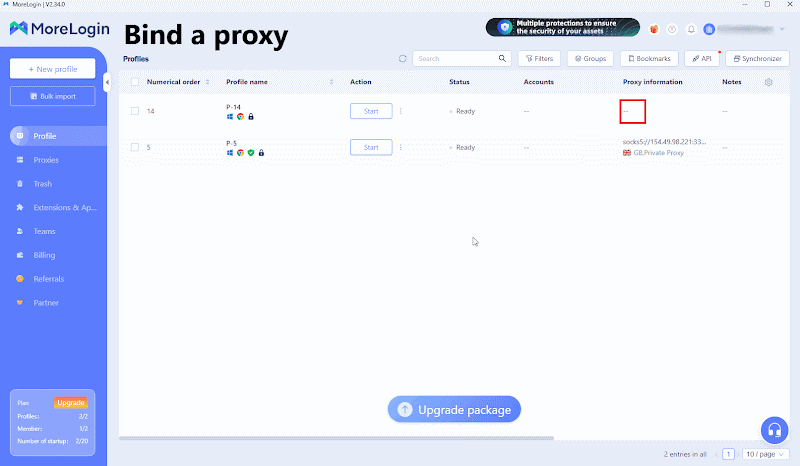
Click the “Proxy Detection” button below to confirm a successful proxy connection.
Save the configuration and run the browser configuration file to securely and anonymously access the target website.
2. Windows
Press Windows + I to open the Settings menu.
Navigate to Network & Internet > Proxy.
In the Manual setup section, toggle Use a proxy server to On; ensure Automatically detect settings is also enabled.
Enter the proxy IP address and port provided by your proxy service.
If you want certain websites to bypass the proxy, add them to the list using a semicolon to separate entries.
Click Save to apply changes.
3. macOS
Click the Apple menu and go to System Preferences.
Select Network and choose the network type (Wi-Fi or Ethernet) you want to configure.
Click Advanced > Proxies.
Choose either Auto Proxy Discovery or Manually configure proxy.
If your proxy requires authentication, select Proxy server requires password and enter your username and password.
Click OK to save the configuration.
4. Android
Go to Settings > Wi-Fi.
Long-press the network you want to change and select Modify Network.
Tap Advanced options and select Manual under the Proxy section.
Enter your proxy hostname and port.
Click Save to apply settings.
5. iOS
Open Settings > Wi-Fi.
Select the current network and scroll to the HTTP Proxy section.
Tap Configure Proxy and choose Auto or Manual.
Input the proxy server address and port.
Click Save.
6. Google Chrome
Chrome allows proxy configuration through system settings or extensions:
Open Chrome and click the menu icon in the top-right corner.
Go to Settings.
In the left sidebar, select System and click on Open your computer’s proxy settings.
Follow the steps for your operating system (Windows or macOS) to configure the proxy server.
7. Microsoft Edge
Edge relies on system settings similar to Chrome:
Open Edge and click the three dots in the top-right corner.
Select Settings > System and performance.
Click Open your computer’s proxy settings.
Follow the Windows steps to configure the proxy.
8. Firefox
Firefox supports independent proxy configuration:
Open Firefox and click the menu button (☰) in the top-right corner.
Go to Settings > General > Network Settings > Settings.
Choose Manual proxy configuration.
Enter the proxy server’s IP address and port in the HTTP Proxy field.
Click OK to save the proxy configuration.
By following these steps, you can easily configure a proxy server on your device or browser.
When selecting a proxy server provider, several factors need to be considered, including:
● Whether the provider offers a diverse range of IP types (residential, mobile, etc.).
● Whether the service guarantees speed and stability.
● Whether there is global geographic coverage.
● Whether the provider ensures compliance with data sourcing regulations.
● Whether customer service and technical support are responsive.
When you want to purchase proxy services, choosing a reliable provider can enhance your experience. Thordata, as one of the most trusted brands for first-time users of proxies, has become the preferred choice for many due to its robust network infrastructure and compliance advantages.
1. Diverse Global Proxy Network
Thordata operates a network of over 60 million residential proxies, covering more than 195 countries and regions. It offers various types of proxies, including residential, mobile, data center, and static ISP, allowing users to flexibly choose based on their specific use cases. With dynamic IP rotation and precise geolocation, users achieve greater flexibility and adaptability.
2. High Performance and Security Assurance
In terms of performance, Thordata maintains a 99.7% uptime and a 99.9% connection success rate, with average latency below 0.5 seconds. Additionally, it employs traffic encryption and a strict zero-log policy, ensuring stable connections while keeping user data and privacy secure.
3. Compliant and Transparent IP Sourcing
Thordata’s proxy IPs are sourced from real household devices, strictly adhering to GDPR and CCPA regulations. This helps businesses conduct data collection and network operations efficiently and legally. Such transparency and compliance give Thordata a high reputation in the industry.
4. Advanced Data and Automation Solutions
Beyond basic proxy services, Thordata also provides advanced data solutions. Through a range of web scraping tools and high-quality datasets, users can easily access and process information, helping businesses maintain a competitive edge in market research, competitive analysis, and intelligent operations.
👍 Note: Thordata offers a free trial!
Through this guide, you should have mastered the methods for configuring a proxy server across various operating systems and browsers. From basic concepts to practical steps, and from risk awareness to leveraging advantages, proxy servers can play a significant role in business operations. We encourage you to choose a suitable proxy solution based on your specific needs and start exploring the various possibilities that proxy servers can offer.
Frequently asked questions
Is a proxy server legal?
Using a proxy server is legal as long as your activities comply with the law and the relevant service terms. For example, businesses often use proxies to improve security or optimize access speed, which is completely legitimate. However, using proxies for hacking, fraud, or data abuse would be illegal.
How do I create my own proxy server?
There are several ways to set up your own proxy server. The most common methods include configuring the built-in proxy functions on Windows or Linux, using open-source tools like Nginx or Squid. This process requires some networking knowledge, such as port management and security rule configuration.
What Are the Types of Proxy Servers?
Main types include HTTP proxies, transparent proxies, and anonymous proxies, each designed for specific use cases such as web browsing or data transmission.
About the author

Anna is a content specialist who thrives on bringing ideas to life through engaging and impactful storytelling. Passionate about digital trends, she specializes in transforming complex concepts into content that resonates with diverse audiences. Beyond her work, Anna loves exploring new creative passions and keeping pace with the evolving digital landscape.
The thordata Blog offers all its content in its original form and solely for informational intent. We do not offer any guarantees regarding the information found on the thordata Blog or any external sites that it may direct you to. It is essential that you seek legal counsel and thoroughly examine the specific terms of service of any website before engaging in any scraping endeavors, or obtain a scraping permit if required.
 Looking for
Top-Tier Residential Proxies?
Looking for
Top-Tier Residential Proxies? 您在寻找顶级高质量的住宅代理吗?
您在寻找顶级高质量的住宅代理吗?
5 Best Etsy Scraper Tools in 2026
This article evaluates the top ...
Yulia Taylor
2026-02-09

What is a Headless Browser? Top 5 Popular Tools
A headless browser is a browse ...
Yulia Taylor
2026-02-07

Best Anti-Detection Browser
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2025-01-22 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-06
What is a UDP proxy?
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2025-01-22 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-06

What is Geographic Pricing?
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2025-01-22 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-05

How to Use Proxies in Python: A Practical Guide
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2025-01-28 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-05

What Is an Open Proxy? Risks of Free Open Proxies
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2025-01-22 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-04

What Is a PIP Proxy? How It Works, Types, and Configuration?
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2025-01-22 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-04
TCP and UDP: What’s Different and How to Choose
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2026-02-03 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-04